Sophos Firewall
- Email Protection -
Email Protection Configuration
Email Protection Modes
Mail Transfer Agent (MTA) Mode
- default mode
- Mail spool
- Mail log
- Zero-day protection
- DKIM
Legacy Mode
- used for XG86
- Sophos Firewall acts as a transparent proxy
Configured in:
PROTECT – Email – General settings
Email Protection configuration process
- Set the SMTP settings, including hostname
PROTECT – Email – General settings - Review TLS settings and configure as required
PROTECT – Email – General settings - Configure host and user relay settings
PROTECT – Email – Relay settings - Enable SMTP relay for the zones you want to accept email from
SYSTEM – Administration – Device access - Optionally, configure the advanced SMTP settings
PROTECT – Email – General settings
Smarthosts
Smarthosts can be used to improve the reliability of your email delivery with outbound relays, allowing you to route email via an alternate set of servers (a smart host), rather than directly to the recipient’s server.
Configured in:
PROTECT – Email – General settings
Email Policies
Policy types
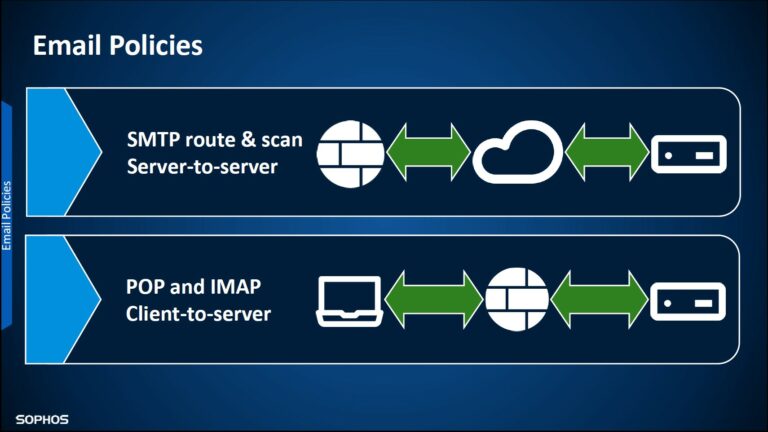
SMTP policies for server-to-server communications, in MTA mode this is SMTP route & scan
IMAP and POP policies for clients downloading emails from mail servers
Data Protection and Encryption
Sophos Firewall can help prevent data being sent out by mistake by scanning the content for sensitive data.
There are predefined content control list (CCLs) created and maintained by SophosLabs.
Secure PDF Exchange (SPX)
Sophos Secure PDF Exchange (SPX) provides an easy way to send encrypted emails without the need to exchange keys or certificates with the recipient.
The original email is converted to a PDF, along with an attachment, and is then encrypted with AES-128 or AES-256
Sophos Firewall will encrypt emails when either:
- The email matches a scanning rule with an action to use SPX
- Or it detects the x-header to encrypt.
The x-header is added by the Sophos outlook plugin when the user clicks the button to encrypt the email
Sophos Outlook Plugin:
CONFIGURE – Authentication – Client downloads
SPX templates
The behaviour of SPX is defined in the SPX template, where you can:
- define the encryption algorithm to use
- choose how the password will be generated and any settings related to that method
- customize email templates that the recipient will see
- Optionally enable the reply portal, which allows recipients to reply securely using a button in the PDF.
SPX templates are configured in:
PROTECT – Email – Encryption
SPX Passwords
- Password specified by sender
Password must be provided in the subject line or the email will fail to send as it cannot be encrypted - System generated passwords
Firewall will generate the password and sent it to the sender to share with the recipient.
Can either be one-time for each email or stored and reused for every email that need to be encrypted for that recipient. - Password specified by recipient
The recipient receives a request to create a password in the registration portal that will be stored and used for that recipient
For sender specified and system generated passwords, the sender is responsible for communicating the password to the recipient. Usually done via a separate channel, for example by SMS or phone.
Quarantine Management
- WebAdmin
- Quarantine digest emails
- User portal
WebAdmin
filter and search the quarantine and either download the email to view or choose to release it.
Note:
Emails that have been detected as containing a virus cannot be released.
Digest Emails
Contains a list of newly quarantined emails that have been quarantined since the last digest along with a link to the User Portal.
Note:
The quarantine digest will be created in the language which is used within the WebAdmin
User Portal
In the User Portal all emails quarantined for that user can be viewed.
Users cannot release emails that are infected.
Users can also manage a personal allow and block list of email addresses and domains.
Note:
Allowed emails will still be checked for malware, but no spam checks.
DomainKeys Identified Mail (DKIM)
DKIM is used to authenticate email servers for a domain and protects email senders and recipients from forgery, sppofing and phising attacks.
When DKIM is applied, recipients can verify that they have received emails from an authorized mail server
How it works:
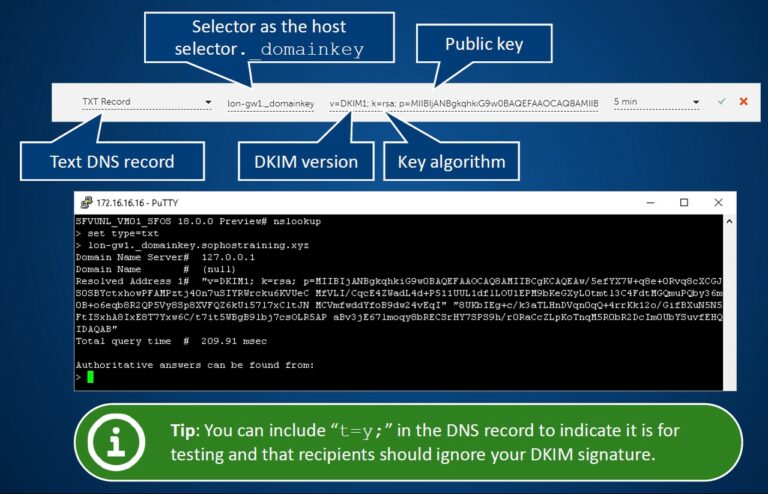
- In the DNS record the domain owner publishes a cryptographic public key.
- When a message is sent, the server generates and attaches a unique DKIM signature to the email message header
- The recipient receives the email and runs a DNS query to search for the sender domains’ public key
DKIM verification for emails that are received can be enabled in:
Email – General settings
Configure DKIM signing
First, you must generate a private and public key pair
Generate a 2048 bit private key:
openssl genrsa -out dkim.key 2048 Extract the public key
openssl rsa in dkim.key out dkim.pub pubout outform PEM Strip unwanted characters from the public key
grep -v -e “^ “^-” dkim.pub | tr -d “\n” > dkim.pubkey 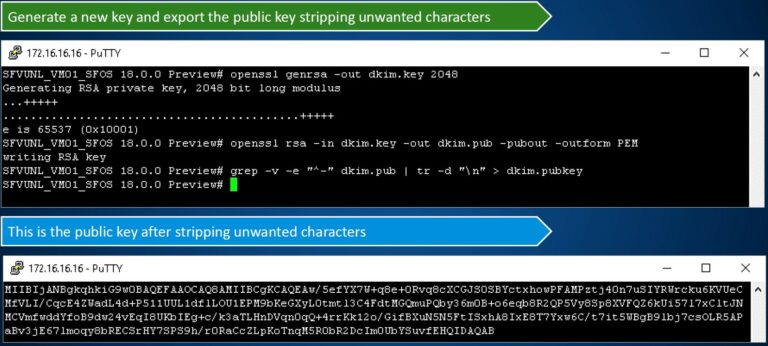
In the WebAdmin you must upload the private key with a key selector that can be used to retrieve the associated public key from DNS.
Email – General settings
Create a DNS record containing the public key that receiving servers can use to verify the signature.
- the host is the selector followed by “._domainkey“